Privacera Connector for AWS Lake Formation¶
AWS Lake Formation is a fully managed service that simplifies the construction, security, and management of data lakes. It provides a permissions model that builds upon the IAM permissions model, enabling fine-grained access to data stored within data lakes through a straightforward grant-and-revoke mechanism, similar to that of a relational database management system (RDBMS). AWS Lake Formation enforces permissions with granular controls at the column, row, and cell levels across various AWS services, including Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Redshift Spectrum.
Synchronization of Policies to Other Data Sources¶
One of the key features of the Privacera Connector for AWS Lake Formation is the ability to synchronize access control policies defined in AWS Lake Formation with other data sources that use the same Glue Catalog. This ensures consistent enforcement of policies across all data sources, providing a unified and centralized approach to data governance.
However, the access control features supported by AWS Lake Formation are not identical to those of other data sources. Therefore, only the policies that are supported by both AWS Lake Formation and the other data sources can be synchronized. For example, since AWS Lake Formation doesn't support dynamic column masking privileges, these policies cannot be enforced in other data sources that do support dynamic column masking. Thus, the policies in AWS Lake Formation in Privacera become the source of truth for those that can be enforced across AWS Lake Formation and other data sources.
Supported Products¶
| Product | Supported |
|---|---|
 Access Management Access Management | Yes |
 Discovery Discovery | No |
 Encryption Encryption | No |
- Since AWS Lake Formation only manages access control policies, Privacera Discovery is not applicable for this connector.
- Since AWS Lake Formation doesn't support dynamic column masking, Privacera Encryption is not applicable for this connector.
Connector configuration modes¶
The following two modes are available for configuring the AWS Lake Formation connector with Privacera.
Push mode¶
In this mode, Privacera serves as the authoritative source for access control policies. These policies are defined within Privacera and then pushed to AWS Lake Formation, where they are enforced across supported services, including Amazon Redshift Spectrum, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Athena.
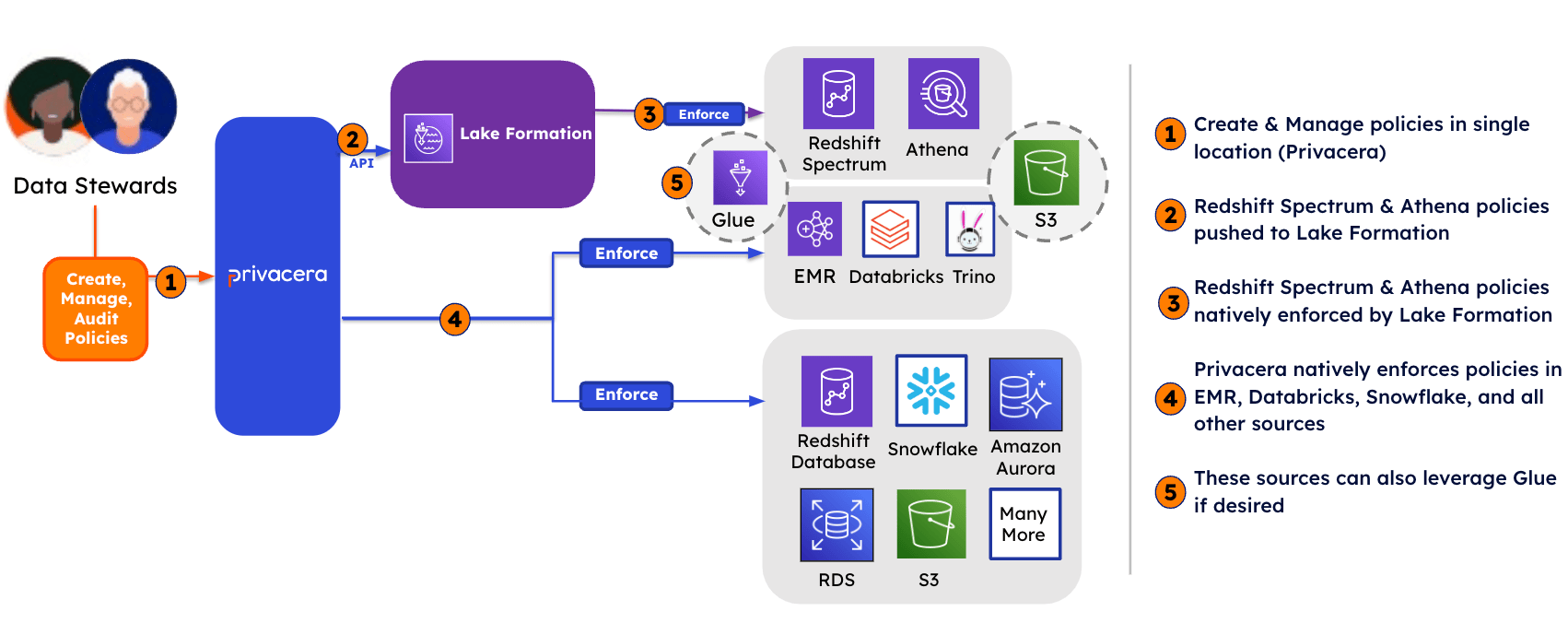
As illustrated in the image above, in Push mode, all policies are stored and managed by Privacera. For databases with metadata stored in Amazon S3 through the AWS Glue Catalog, Privacera pushes the policies to AWS Lake Formation using Lake Formation APIs. AWS Lake Formation then enforces these policies natively. For the remaining data sources, Privacera uses its connector architecture to enforce the policies.
Since the same databases and tables defined in AWS Glue could be used by other third-party tools, such as Databricks and Trino, the same policies can also be optionally enforced by these tools. Please note, in this case, the capabilities.
Pull mode¶
In this mode, AWS Lake Formation serves as the authoritative source for access control. Access control policies are retrieved from Lake Formation at specified time intervals. These policies are then enforced by Privacera on various data sources as defined by the provided configuration.
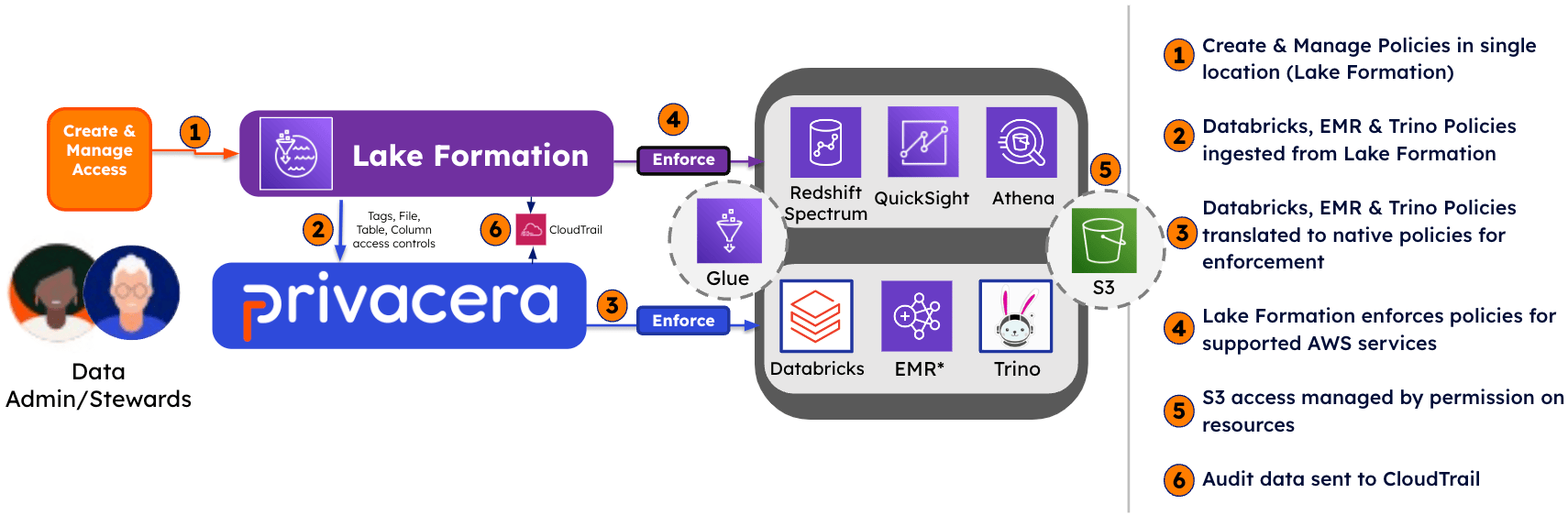
As illustrated in the image above, in the Pull mode, AWS Lake Formation functions as the enforcement layer for datasets in S3 that have their metadata stored in the Glue Catalog. Since AWS Lake Formation serves as the enforcement layer, administrators will manage these policies directly within the AWS Lake Formation console or through its APIs. Given that the same databases and tables defined in AWS Glue may also be utilized by third-party tools such as Databricks and Trino, it is imperative that the same policies are consistently enforced across these platforms as well.
Privacera offers native integrations with most tools that utilize AWS Glue, enabling the enforcement of access control policies. This process involves retrieving policies and tags from AWS Lake Formation and transferring them to Privacera. Once these policies and tags are in Privacera, the platform enforces them in Databricks and/or Trino by applying the same policies defined in AWS Lake Formation.
Comparison of Pull and Push Mode¶
To help you choose the correct mode for using the Privacera connector for Lake Formation, the table below outlines the key differences between the Pull and Push modes:
| Feature | Pull Mode | Push Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Data Flow Direction | Pulls data from Lake Formation into Privacera | Pushes data from Privacera to Lake Formation |
| Data Access Management | Privacera periodically fetches access control lists (ACLs) from Lake Formation | Privacera directly updates ACLs in Lake Formation |
| Real-time Updates | Not real-time; depends on the polling interval | Real-time updates as changes are pushed instantly |
| Latency | Higher latency due to periodic polling | Lower latency with immediate policy enforcement |
| Tag and Masking Support | Pulls tags and tag resource mapping from Lake Formation | Limited to Lake Formation capabilities. Tag-based and Resource-based masking are not supported, since LF does not expose APIs to support them |
| Use Case Suitability | Use this if you are already using Lake Formation and want to replicate the policies to other data sources that use the same Glue catalogs, like Databricks and Trino | Use this if you want to manage the policies for all data sources from one central point in Privacera |
Note
- In Pull mode, Privacera pulls tags and tag resource mapping from Lake Formation.
- In Push mode, masking capabilities are not available, as Lake Formation does not expose APIs to support them.
Recommendation¶
We recommend using the Push mode for the Privacera connector for Lake Formation. Here are the key reasons for this recommendation:
-
Real-Time Policy Enforcement: Push mode enables immediate updates to access control lists (ACLs) in Lake Formation, ensuring that any changes to data governance policies are applied instantly across all integrated data sources. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and enhances data security.
-
Centralized Management: With Push mode, you can manage policies for all data sources from a single, central point. This simplifies the administration of data governance policies and ensures consistency across your entire data ecosystem.
-
Better Control Over Policies: Push mode allows for more granular control and immediate enforcement of policies in Lake Formation. This ensures that data governance rules are consistently applied without delays, enhancing overall compliance and security.
While Pull mode can be useful in specific scenarios, such as replicating policies to other data sources using the same Glue catalog, Push mode offers significant advantages in terms of real-time updates, centralized management, and enhanced control and security. Consequently, for most use cases, Push mode is the preferred option for ensuring robust and efficient data governance with the Privacera connector for Lake Formation.
Transitioning from Pull Mode to Push Mode¶
For those who want to start with Pull mode and later transition to Push mode, the process is straightforward and can be managed effectively with the following steps:
-
Initial Setup in Pull Mode:
- Begin by setting up the Privacera connector in Pull mode to integrate with Lake Formation.
- Configure the connector to periodically fetch access control lists (ACLs) from Lake Formation.
- Define and implement your data governance policies, ensuring they are replicated to other data sources that use the same Glue catalogs, like Databricks and Trino.
-
Monitor and Evaluate:
- Regularly monitor the performance and effectiveness of the Pull mode setup.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders on the current setup's effectiveness and areas for improvement.
-
Prepare for Transition to Push Mode:
- Plan the transition by outlining the necessary changes and ensuring all stakeholders are informed.
- Review the prerequisites for Push mode
- Update your data governance policies to ensure they are ready for real-time enforcement.
-
Transition to Push Mode:
- Reconfigure the Privacera connector to operate in Push mode. This involves setting up direct updates of ACLs from Privacera to Lake Formation.
- Ensure that the connector is correctly pushing policy changes in real-time and that all configurations align with your initial setup.
- Test the new configuration to verify that policy updates are being applied instantly and consistently across all integrated data sources.
-
Post-Transition Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor the performance of the Push mode setup.
- Address any issues or challenges that arise during the transition to ensure a smooth operation.
Once you're ready to leverage the benefits of real-time updates and centralized management, transitioning to Push mode will enhance your data governance capabilities and ensure more robust security and compliance across your data ecosystem.